Fast Prototyping In Design Thinking – A Closer Look!
Fast Prototyping In Design Thinking – A Closer Look!
While you order your N-95 masks, gloves, and sanitizers online, here is a proposition – have you noticed that this COVID-19 brought with it an accelerated move towards the e-commerce world?
Each business, irrespective of the genre of their trade, are leaning heavily towards building an online shop to grab on the potential clients in the digital platform. Subsequently, there has been increased competition to design websites among businesses. A tendency to create unique and appealing websites is all that trades look into.
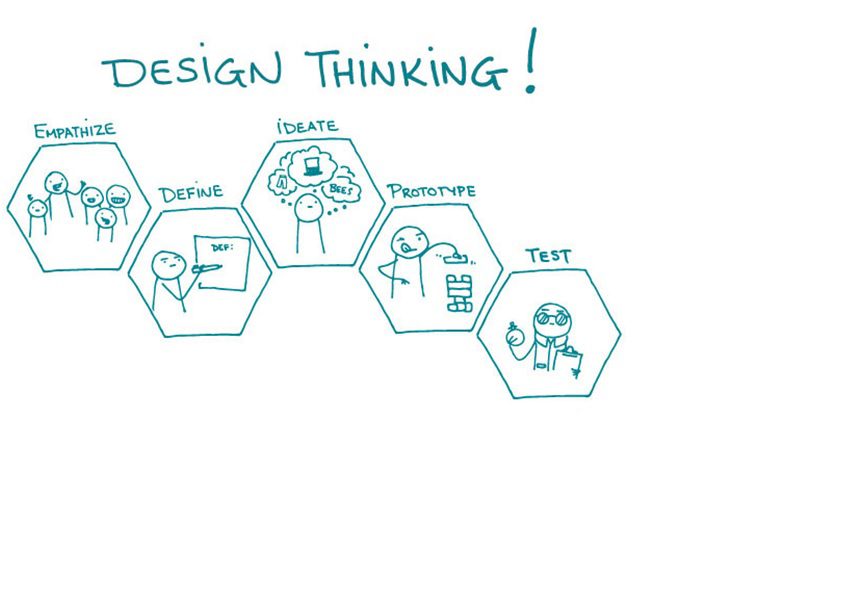
Enterprises, in an expectation to possess crispy and trending website designs, put their trust in professional web design companies. Such designing companies follow the design thinking approach – a process and ideology that is used to resolve complex issues, with the customer-centrism approach. The process takes on a solution-based approach and is divided into 5 phases –
Phase I: Empathize
Phase II: Define
Phase III: Ideate
Phase IV: Prototype
Phase V: Test
For this article, the focus point is Stage 4 – Prototyping. While design thinking is not a linear process, each step throws light on new discoveries, and in this process, the Prototyping stage is a crucial one. Here are the details on it –
Stage 4 In Design Thinking: Prototyping – What Is It?
Remember Mark I, II, and III? Yes, you got it right! These were prototypes for the Iron Man suit by Tony Stark!
Think of this, even Mr. Stark needed prototypes, a.k.a., testing – then why wouldn’t your site’s designs?
Prototyping is a proposed solution that is used to validate or test design implementations or ideas. This simple experimental model takes into account if the implemented solutions are successful. The yielded results reflect issues that might have been established towards the introductory phase of the project. These results are put to use via the building of a robust understanding of such issues while interacting with products.
The scaled-down versions of products, or prototypes, are used to –
- Record
- Observe
- Judge
- Measure
-a user’s interaction, behavior, or reaction to the product design.
This offers designers a different perspective on the product design so that any failure with the design does not give way to considerable financial or time-related strains. Such slowing down to speed up the procedure is an approach to ensure cost-effective failures.
What Are The Types Of Prototyping?
Based on the type of functionalities and model built-in, prototypes are categorized into types –
A. Functional Prototype
Such prototypes are targeted to imitate the functionalities of original products. Often, their appearance does not match up to that of the original product, only its inner working is accurate to the T.
B. Miniature Prototype
Smaller versions of the actual product are put to use here. Such prototypes focus on both aspects – display and functionality.
C. Display Prototype
In the display prototypes, the major focus is on the feel and look of products and not on its functionality.
Based on Usability
·Throwaway Prototype
In throwaway prototypes, the models only reflect the working potential of the product in discussion and are hence often discarded after the testing.
·Evolutionary Prototype
Developers build in basic prototypes that are further enhanced. These models are built to form origin saleable products to avoid any resource wastage.
Based On Completeness
·High-Fidelity Prototyping
These models include operation with final products. The developed prior-version of the software is put to use and programs for designing are implemented like Adobe Illustrator or Sketch.
·Low-Fidelity Prototyping
It comprises the use of basic examples or models in product testing. Subsequently, the yielded prototype is conveniently made, inexpensive, or is visualizations of the same. This includes examples like card sorting, storyboarding, and sketching.

Why Do You Need The Power Of Prototyping?
While prototyping is a necessary stage in the Design Thinking process, multiple brands often skip it, considering it to be a phase that slows down the project. However, there are multiple pros of this procedure that are well-explained over its qualities –
1. Precision
Prototyping is all about acquiring precision of the product, and on a whole, of the project in hand. This is well defined by the fidelity of prototyping – low and high fidelity. This reflects on the realism, detail-levels, and the design of the product.
2. Representation
This quality of prototyping is all about the keynote uses and the presentation of the product. This includes a categorization of the prototype structuring that involves – digital, paper, or code.
3. Evolution
This prototyping quality involves the lifecycle of the prototype. While some prototypes are structured to be designed, analyzed, and thrown away, while others are reiterated unless and until the aspects are worked upon and refined or precisely worked upon.
4. Interactivity
The interactivity quality of the prototyping is largely based on the user and the experience that they gather from the usage of the product. It takes into consideration whether the prototype is partially or fully functional or there are no interactions at all. Alterations are made to the product, based on such deductions.
How Does Prototyping Work?
Since the importance of prototyping is well-established, brands are now leaning towards this step in Design Thinking. Enterprises are now looking up to experts in the field like the best website design in New York, to acquire the proficiency in prototyping. Efficiency, time-efficient and consumer awareness are the various pros for this phase and are created in the following way –
1. Choosing A Prototype
Prior to creating a prototype, it is important to take into consideration –
- The stage of designing
- Available time
- Resources at disposal
For early-phase designing, opting for low-fidelity prototypes, while for products closing in on the product shipping phase, high-fidelity prototypes are ideal.
2. Setting A Goal
Prototypes are launched with a goal for the product. It is essential to set this goal first with client-centrism at its focus. Make sure that your opted prototype is potent enough or aimed at giving the desired results.
3. Using The Appropriate Tools
This runs true, especially for digital prototyping. It is mandatory to look for tools that would meet the required functionality and features. Make sure to acknowledge the interface of the opted tools to ease the process.
4. Taking The Action
The Design thinking process is not a linear procedure and hence, prototyping can be carried out when and how required. Generate ideas and while designing them, make sure to test them from time to time.
What Are The Various Prototyping Methodologies?
In case you are wondering how to design a prototype product, there are majorly three kinds of prototyping methodologies that include –
A. HTML Prototyping
For individuals who are well-versed in HTML, this is the best methodology. However, considering that this is a time-consuming process, it becomes a cumbersome process to follow. This methodology often becomes redundant during the early or mid-stage while creating designs since they require occasional alterations.
B. Paper Prototyping
Considered ideal for early-stage prototyping, this methodology lasted for a long time. All that is required in this methodology is pen and paper for this prototype design and boosts team bonding wherein the innovation of each team member is hailed. However, designing on paper brings with it multiple cons, one of which is the unrealistic character of the model that makes offering feeding a challenging process.
C. Digital Prototyping
The most common prototyping methodology, this involves a realistic design that helps in the reiteration and feedback process for designs. This method is beneficial for understanding the flow to stakeholders and users and ensures enhanced interaction.
Steps To Implement Fast Prototyping
Implementing fast prototyping is an attempt to make the ideas tangible, get quicker feedback, and learn in the process. Such rapid testing via the real clients ensures that the final product delivered is one with errors and caters to the evolving needs of customers.
The steps involved in implementing such fast prototyping are as follows –
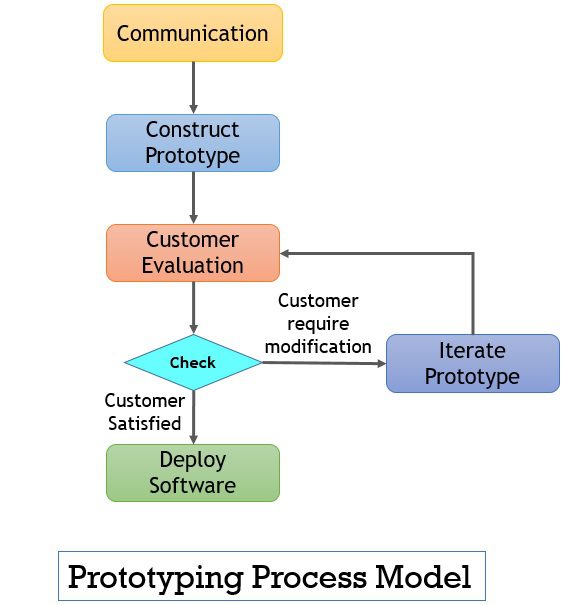
Step 1: Brainstorm Ideas
The ideas conceived are bundled into concepts and developers and designers will now need to select the ones that they want to test.
Step 2: Build And Run Prototypes
Consider that ‘what to prototype’ has been finalized, the second step is building and running the prototypes. The results ensure that developers have access to the fastest testing ways.
Step 3: Use Prototype Report Card Worksheet
Often, multiple prototypes are tested simultaneously. In order to streamline and organize the findings and learn about which iterations will need your focus, it is essential to use a prototype report card worksheet.
Step 4: Integrate Feedback And Iterate
Prototyping is not a single process, but a reiterative one. The sequence is repeated to improve and refine the findings. In this endeavor, developers rely on a feedback and reiteration prototype design process that ensures the focus on the findings.
Conclusion
Prototyping and testing run simultaneously and requires feedback from the real users to take into account their interaction with the designed product. The current product is then subjected to alterations based on the review. Such informed decisions on designing ensure user-friendly product designing that cater to the user’s requirements. So, go ahead! Make your product design prototype and build upon the feedback!
